In this article we will discuss about assimilation and cognitive development theory by Jean Piaget. The growth of children will experience four key stages of cognitive development as per psychologist Jean Piaget. In every stage, there is a shift in the understanding of the world by the kids. Children explore everything around them and try to make sense of the world like little scientists.

What Is Assimilation?
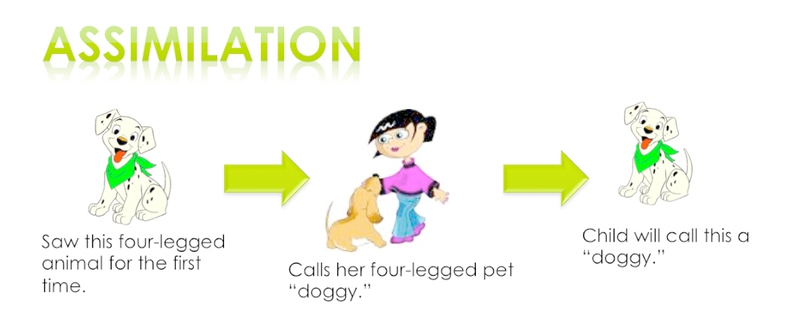
The cognitive process by which new information is fit into existing cognitive schemas, perceptions and understanding is called as assimilation. Adaptation to new experiences and information can be done in two basic ways according to Piaget. The easiest method is assimilation because in this a lot of adjustment is not required. So when you receive new information, you refer to the information you have already processed and learned and make sense of the new information.
Examples:
Students are good at working with computers and easily learn navigation of new websites and programs.
When a child sees a new type of dog which he has never seen before, he points to it referring it as "Dog".
A chef learns a new cooking technique.
A computer programmer learns a new programming language.
A child sees a zebra for the first time and refers to it as a horse, assimilating the information into the schema for a horse.
A child learns to call her father daddy, and calls other males also daddy.
Other Key Concepts in Jean Piaget's Cognitive Development
Schemas
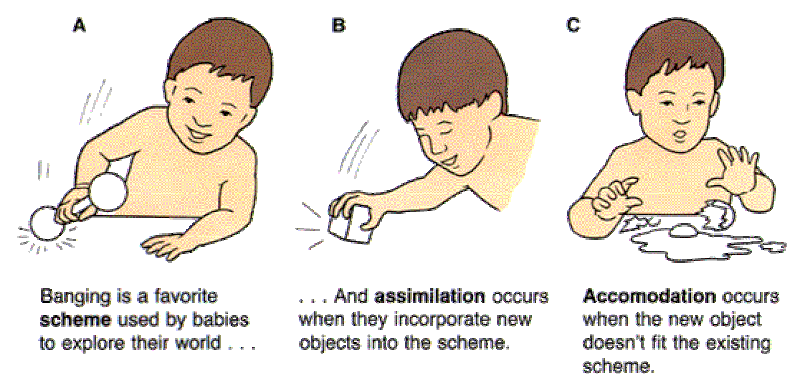
Schema involves both mental and physical actions in understanding and knowing. They are categories of different knowledge which helps us to interpret and understand the world. For example, a child may create a schema about a dog. If the child has seen only small and furry dogs, he might believe that all dogs are small and furry. In such a scenario, when the child comes across a large dog, he will take in the new information and modify the existing schemas to make changes as per the new observations.
Accommodation
Changing or altering the existing schemas when new information is received is called as accommodation. It involves altering existing schemas or ideas when new experiences come into picture. In such a scenario, new schemas are also formed. By looking at the example below, we can understand the different between assimilation and accommodation.
Your neighbor’s daughter is a very sweet, polite and kind girl. One day you look out of the window to find her throwing snowballs at your car, which seems very rude and out of character for the girl. By the process of assimilation, you will ignore the girl’s behavior, believing that she does not mean to be impolite. But, by the process of accommodation, the girl’s behavior will cause you to reevaluate your opinion of her.
Equilibration
Piaget held the opinion that children strike a balance between assimilation and accommodation. And this balance is achieved by a mechanism called as equilibration. As the progress through the stages of cognitive development happens, it is important to maintain a balance between assimilation (using previous knowledge) and accommodation (adding new knowledge to previous knowledge). Children move from one stage of thought to the next by means of equilibration.

View All Comments /Add Comment